JAC Board Class 9th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
JAC Class 9th Geography Natural Vegetation and Wildlife InText Questions and Answers
Activity (Page No. 43)
Question 1.
Why are the southern slopes in Himalayan region covered with thick vegetation coyer as compared to northern slopes of the same hills?
Answer:
Northern slopes of the Himalayan region are mostly covered with snow due to its high altitude. On the other hand, southern slopes receive heavy rainfall and soils found here are suitable for plant growth. Therefore, southern slopes have thicker forests as compared to northern slopes of the Himalayan region.
![]()
Question 2.
Why have the western slopes of the Western Ghats covered with thick forests and not the eastern slopes?
Answer:
Western slopes of the Western Ghats receive more than 300 cm of rainfall, while the eastern slopes fall in the rain shadow area and receive only 50-60 cm of rain¬fall. Therefore, forests of western slopes have luxuriant growth as compared to eastern slopes of the Western Ghats.
Activity (Page No. 43)
Question 1.
Celebrate Van Mahotsav in your school/locality and plant few saplings and notice their growth.
Answer:
Students, please do it yourself.
Activity (Page No. 43)
Question 1.
Study the bar graph (Figure 5.1) and answer the following questions.
1. Name the state having maximum area under forest cover.
2. Name the union territory having minimum area under forest cover and why?
Answer:
- Mizoram
- Daman & Diu. In Daman and Diu, the area under forest is merely 5.72% because of the following reasons:
(a) Most of the area is industrialized and the rest is residential.
(b) The total area of Daman & Diu is very small amounting to only 102 sq. metres.
Activity (Page No. 47)
Question 1.
1. What will happen if plants and animals disappear from the earth’s surface?
2. Can the human beings survive under such a situation ?
3. Why is bio-diversity necessary and why should it be conserved ?
Answer:
- If plants and animals disappear from the earth, the ecological balance will be disturbed and life would become miserable. The existence of humans will not be possible.
- No, the human beings cannot survive under such a situation. It is because all plants and animals species including humans are interdependent.
- Bio-diversity is necessary because it provides many essential things for the survival of human beings. It should be conserved because our ecosystem has been badly damaged due to the uninterrupted and excessive exploitation of plant and animal resources in our country.
Activity (Page No. 48)
Question 1.
Can you identify the type of forest shown in this picture ? Identify some trees in it. What type of similarity/dissimilarity you notice in this type of vegetation from the one found in your region ?
Answer:
Yes, these are montane forests.
Some trees which is seen are deodar, pine, spruce and cedar.
I reside in Rajasthan where species of bushes and thorny forests are mostly found, such as Acacias, euphorbias and cacti etc.
Activity (Page No. 50)
1. Find out from the above newspaper cuttings, the main concern highlighted in the given news items.
2. Collect more information about various endangered species from newspapers and magazines.
3. Find out various steps taken by the Indian government to protect them.
4. Describe how you can contribute to the protection of endangered animals and birds.
Answer:
- Dwindling number of wildlife species vulture, tiger and rhinoceros.
- Do it yourself.
- Various steps taken by the Indian government to protect the wildlife are:
- 89 National parks, 543 Wildlife sanctuaries and Zoological gardens have been set up to take care of natural heritage.
- Project Tiger, Project Rhino, Project Great Indian Bustard and many other eco-developmental projects have been introduced.
- 18 biosn’iere reserves have been set up in the country to protect flora and fauna.
- Financk and technical assistance is provided to many Botanical Gardens by the government since 1992.
- We can do Lie following:
- Use of print and mass media to spread awarness,
- Create pul lie awareness through lectures, railies, nukkad nataks, etc.
- Organise poster/drawing competitions.
JAC Class 9th Geography Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below:
1. To which one of the followihg types of vegetation does rubber belong to?
(a) Tundra
(b) Tidal
(c) Himalayan
(d) Tropical Evergreen.
Answer:
(d) Tropical Evergreen.
2. Cinchona trees are found in the areas of rainfall more than:
(a) 100 cm
(b) 50 cm
(c) 70 cm
(d) less than 50 cm.
Answer:
(a) 100 cm
3. In which of the following state is the Simlipal bio-reserve located?
(a) Punjab
(b) Delhi
(c) Odisha
(d) West Bengal.
Answer:
(c) Odisha
4. Which one of the following bio-reserves of India is not included in the world network of bioreserve ?
(a) Manas
(b) Nilgiri
(c) Gulf of Mannar
(d) Nanda Devi
Answer:
all of these options are included in the world network of bioreserves.
![]()
Question 2.
Answer the following questions briefly:
1. What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
Answer:
Factors responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India are:
- Land
- Soil
- Temperature
- Photoperiod (sunlight)
- Precipitation.
2. What is a bio-reserve? Give two examples.
Answer:
A protected area reserved for the conservation of endangered species of flora (plants) and fauna (animals) in their natural habitat. The Sunderbans in West Bengal and Nanda Devi in Uttaranchal are two examples.
3. Name two animals having habitat in tropical and montane type of vegetation.
Answer:
- Tropical vegetation Elephant, deer.
- Montane vegetation Yak, Snow leopard.
Question 3.
Distinguish between:
1. Flora and fauna,
2. Tropical evergreen and deciduous forests.
Answer:
1. Distinction between Flora and Fauna:
| Flora | Fauna |
| 1. Flora is the term used to denote plants of a particular region. | 1. Fauna is the term used to denote animals of a particular region. |
| 2. Flora consists of grass, plants, creepers and trees. | 2. Fauna consists of three types: (a) Ter – restrial animals, (b) Aquatic animals and (c) Aerial. |
| 3. About 47,000 plant species are found in India. | 3. About 90,000 animal species are found in India. |
| 4. Almost flora species produce their own food. | 4. No animal can produce its own food. |
| 5. Flora provides food to all living or-ganisms. | 5. Fauna provides nutrients to the soil from its waste and decay. |
2. Distinction between Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous Forests :
| Tropical Evergreen Forests | Tropical Deciduous Forests |
| 1. These are found in areas having more than 200 cm of rainfall. | 1. These are found in areas having rainfall between 200 cm and 70 cm. |
| 2. The trees of these forests do not shed their leaves in a definite time. | 2. The trees of these forests shed their leaves for about six to eight weeks in dry summer. |
| 3. The trees reach great heights up to 60 metres or even above. | 3. The trees reach heights up to 9 metres. |
| 4. These are found in heavy rainfall areas of the Western Ghats and the island groups of Lakshadweep, Andaman and Nicobar, upper parts of Assam and Tamil Nadu coast. | 4. These forests exist in north-eastern states, along the foothills of the Himalayas, Jharkhand, West Odisha and Chhattisgarh and on the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats. |
| 5. Some of the important trees of this forest are ebony, mahogany rosewood, rubber and cinchona. | 5 Important trees of this forest are teak, sal, shisham, bamboos, sandalwood, khair, kusum, arjun and mulberry. |
| 6. The common animals found in these forests are elephants, monkey, lamb, deer, one-horned rhinoceros etc. | 6. The common animals found in these forests are lion, pig, deer, elephant lizards, snakes and tortoises. |
![]()
Question 4.
Name different types of vegetation found in India and describe the vegetation of high altitudes.
Answer:
The following major types of vegetation may be identified in India:
- Tropical Evergreen forests,
- Tropical Deciduous forests,
- Tropical thorn forests and scrubs,
- Montane forests, and
- Mangrove forests.
The vegetation found on high altitudes is known as montane vegetation. The chief characteristics of these forests are:
- The wet temperate type of forests are found between a height of 1000 metres to 2000 metres. Evergreen broad-leaf trees such as oaks and chestnuts predominate.
- Between 1500 metres and 3000 metres, temperate forests containing coniferous trees like pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce and cedar are found.
- At high altitudes, generally more than 3600 metres above sea level, temperate forests and grasslands give way to the alpine vegetation. Silver fir, junipers, pines and birches are the common trees of these forests. Ultimately, through shrubs and scrubs they merge into alpine grasslands.
- At higher altitudes, mosses and lichens form part of tundra vegetation.
Question 5.
Quite a few species of plants and animals are endangered in India. Why?
Answer:
Endangered species of plants and animals are those which face the danger of getting extinct. About 1300 plant species and quite a few animal species have been identified as endangered species in India. The main causes for these plants and animals species becoming endangered are as follows:
- Hunting by greedy hunters for commercial purposes.
- Pollution due to chemical and industrial wastes, acid deposits etc.
- Introduction of alien species causing imbalance in the ecosystem.
- Reckless cutting of plants and trees to bring land under cultivation, expanding industrialisation and habitation etc.
Question 6.
Why has India a rich heritage of flora and fauna?
Answer:
India has all the major physical features of the earth, i.e., mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands. These five factors are suitable for the growth and development of both animal and plant kingdom in India and are essential for the growth of the bio-diversity.
The different regions of the country have different soil types, different types of climate with great variations in humidity and temperature across the country. Even the rainfall is also unevenly disturbed, and various types of species of plants and animals require different climatic conditions and different soil types. Hence, the flora and fauna found in India is diverse and rich.
On an outline map of India, label the following:
- Areas of Evergreen Forests,
- Areas of Tropical Deciduous Forests.
- Two national parks each in northern, southern, eastern and western parts of the country.
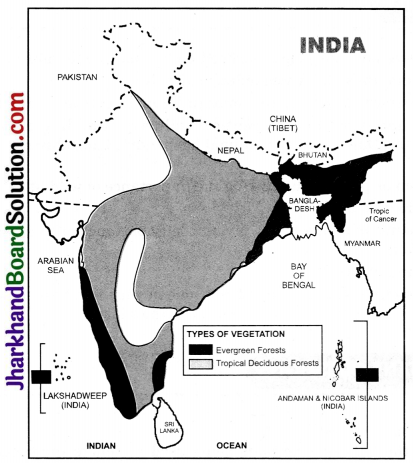
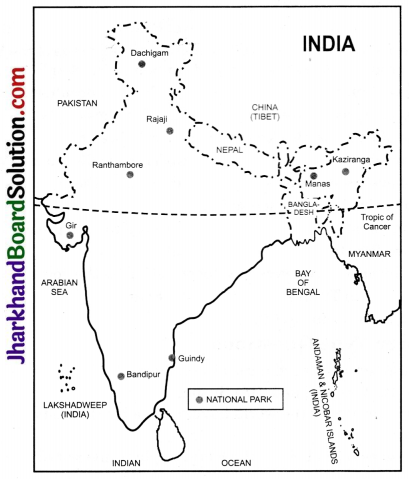
Question 1.
Find some trees in your neighbourhood having medicinal values.
Answer:
Jamun, Neem, Babool, Sarpagandha, Tulsi etc.
Question 2.
Find ten occupations getting raw material from forests and wildlife.
Answer:
Furniture industry, Pharmaceutical industry, Building construction, Leather industry, Meat industry, Dairy industry, Animal husbandry, Lac industry, Sport and Chemical industry etc.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a poem or paragraph showing the importance of wild life.
Answer:
Students, do it yourself.
Question 4.
Write the script of a street play giving the importance of tree plantation and try to enact it in your locality.
Answer:
Students, do it yourself.