JAC Board Class 7th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 4 Air
JAC Class 7th Geography Air InText Questions and Answers
Page 21
Question 1.
Is global warming a serious issue in today’s world?
Answer:
Concern about climate change is much less pervasive in the United States, China and Russia than among other leading nations. Just 44% in the U.S. and Russia, and even fewer in China (30%), consider global warming to be a very serious problem.
Page 23
Question 2.
For ten days note down weather report from a local newspaper and observe the changes occurring in the weather.
Answer:
Students need to do it by their own.
![]()
JAC Class 7th Geography Air Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
(i) What is atmosphere?
Answer:
Atmosphere is a huge layer of air that surrounds the earth. It shields and guard us from the harmful rays of the sun. rays of the sun. rays of the sun.
(ii) Which two gases make the bulk of the atmosphere?
Answer:
The two gases which make the bulk of the atmosphere are nitrogen (78% ) and oxygen (21%).
(iii)
Which gas creates greenhouse effect in the atmosphere?
Answer:
The gas which creates greenhouse effect in the atmosphere is carbon dioxide.
(iv) What is weather?
Answer:
An hour to hour, day to day condition of the atmosphere is called as the weather. It is the total atmospheric conditions of a particular place at a particular time regarding temperature, air pressure, clouds, wind, humidity, etc.
(v) Name three types of rainfall?
Answer:
Three types of rainfall are:
- Convectional rainfall
- Orographic rainfall
- Cyclonic rainfall
(vi) What is air pressure?
Answer:
Air pressure is the pressure which is exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface.
Tick (√) the correct answer.
Question 2.
(i) Which of the following gases protects us from harmful sun rays?
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Ozone
Answer:
(c) Ozone
(ii) The most important layer of the atmosphere is
(a) Troposphere
(b) Thermosphere
(c) Mesosphere
Answer:
(a) Troposphere
(iii) Which of the following layers of the atmosphere is free from clouds?
(a) Troposphere
(b) Stratosphere
(c) Mesosphere
Answer:
(b) Stratosphere
![]()
(iv) As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure
(a) Increases
(b) Decreases
(c) Remains the same
Answer:
(b) Decreases
(v) When precipitation comes down to the earth in the liquid form, it is called
(a) Cloud
(b) Rain
(c) Snow
Answer:
(b) Rain
Question 3.
Match the following.
| (i) Trade winds | (a) Incoming solar energy |
| (ii) Loo | (b) Seasonal wind |
| (iii) Monsoon | (c) Horizontal movement of Air |
| (iv)Wind | (d) Layer of ozone gas |
| (e) Permanent wind | |
| (f) Local wind |
Answer:
| (i) Trade winds | (e) Permanent wind |
| (ii) Loo | (f) Local wind |
| (iii) Monsoon | (b) Seasonal wind |
| (iv) Wind | (c) Horizontal movement of air |
Question 4.
Give reasons.
- Wet clothes take longer time to dry on a humid day?
- Amount of insolation decreases from equator towards poles?
Answer:
1. The air is full of water vapour on a humid day. So, the evaporation is very slow due to low temperature. That’s why, wet clothes take longer time to dry on a humid day.
2. On equator, insolation comes through on vertical rays. So, it covers up less amount of space but more heat is felt when it goes up from equator towards poles and the sun rays become slanting. Though slanting rays heat up more amount of space, the level of hotness is felt less. That’s why, amount of insolation decrease from equator towards poles.
Question 5.
(For Fun)
(i) Solve this crossword puzzle with the help of given clues:
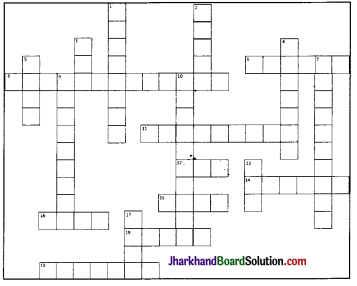
Across:
6. An Indian tree having extraordinary quality of providing oxygen round the clock
8. Gas present in atmosphere occupying only 0.03% by volume
11. Outermost layer of atmosphere
12. Mixture of many gases
14. Life giving gas
15. Air in motion
16. An indian tree valued highly for medicinal properties
18. Gas protecting us from harmful sun rays
19. Low pressure area
Down
1. Amount of water vapour in air
2. Condensation of water vapours around dust particles in atmosphere
3. Example of local wind blowing in summer in northern india
4. Short term changes in atmosphere
5. Precipitation in liquid form
7. Blanket of air around the earth
9. Instrument to measure pressure
10. Incoming solar radiation
13. Reduces visibility in winters
17. It is time when sun is overhead
Answer:
Across:
6. Peepal
11. Exosphere
14. Oxygen
16. Neem
19. Cyclone
Down:
1. Humidity
3. Loo
5. Rain
9. Barometre
10. Insolation
17. Noon
8. Carbon dioxide
12. Air
15. Wind
18. Ozone
(ii) Make a weather calendar for one week. Use pictures or symbols to show different types of weather. You can use more than one symbol in a day, if the weather changes. For example, the sun comes out when rain stops. An example is given below:
Answer:
Hint: Students can do it in this manner.
JAC Class 7th Geography Air Important Question and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
In the atmosphere, the most abundant gas is
(a) Oxygen
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Helium
Answer:
(c) Nitrogen
Question 2.
The winds which below constantly throughout the year in a particular direction is known as
(a) Local winds
(b) Seasonal winds
(c) Permanent winds
(d) None of the these
Answer:
(a) Local winds
![]()
Question 3.
An hour to hour, day to day condition of the atmosphere is known as
(a) temperature
(b) weather
(c) climate
(d) degree
Answer:
(b) weather
Question 4.
Exosphere is the layer of the atmosphere.
(a) uppermost
(b) middle
(c) lower most
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) uppermost
Question 5.
The thermosphere extends between
(a) 90 – 370 km
(b) 100 – 350 km
(c) 50 – 300 km
(d) 80 – 400 km
Answer:
(d) 80 – 400 km
Question 6.
The balance of and gets disturbed, if we cut down trees and forests.
(a) oxygen, helium
(b) nitrogen, heiium
(c) oxygen, carbon dioxide
(d) oxygen, nitrogen
Answer:
(c) oxygen, carbon dioxide
Question 7.
The air which we inhale and exhale means breathe exists in the
(a) mesosphere
(b) stratosphere
(c) troposphere
(d) exosphere
Answer:
(c) troposphere
Question 8.
The instrument which measures the temperature is
(a) Barometer
(b) Thermometer
(c) Wind vane
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Thermometer
Question 9.
In the atmosphere, the ozone layer exists in the
(a) Stratosphere
(b) Exosphere
(c) Mesosphere
(d) Troposphere
Answer:
(a) Stratosphere
Question 10.
The other name of greenhouse gas is
(a) oxygen
(b) nitrogen
(c) argon
(d) carbon dioxide
Answer:
(b) nitrogen
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by smog?
Answer:
Smog is the combination of smoke and fog. It generally occurs during winter season.
Question 2.
What will happen if there is very less rainfall?
Answer:
Water scarcity and drought occurs if there is very less rainfall.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the various forms of precipitation?
Answer:
Various forms of precipitation are rain,snow, sleet and hail.
Question 4.
Give a word/term for the hot and dry wind of northern plains of India.
Answer: Loo.
Question 5. Air pressure is highest at which area?
Answer:
Air pressure is highest at the sea level
Question 6.
What are the three types of winds?
Answer:
The three types of winds are:
- Permanent winds
- Seasonal winds
- Local winds.
Question 7.
When air is heated, what occurs?
Answer:
Air expands and becomes lighter and goes up when the air is heated.
Question 8.
Ozone layer is important for us. Why?
Answer:
Ozone layer is important for us because it protects and shields us from harmful reactions and effects of the sun rays.
Question 9.
Green plants use carbon dioxide. Why?
Answer:
Green plants use carbon dioxide because it helps them to prepare their food and release oxygen.
Question 10.
What is the consequence and importance of greenhouse gas?
Answer:
The consequence and importance of greenhouse gas is that the earth would have been too cold to live in.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the instruments called for the measurement of air pressure and the measurement of amount of rainfall?
Answer:
The instruments are called as barometer for the measurement of air pressure and rain gauge for the measurement of amount of rainfall.
Question 2.
What do you mean by a climate of a place or area?
Answer:
The average weather condition of a place or area for a longer period of time constitutes the climate of a place.
Question 3.
What are permanent winds?
Answer:
Winds which blow constantly throughout the year in a particular direction is called as the permanent winds. The trade wind, westerlies and easterlies are the permanent winds.
Question 4.
What is the role of water vapour?
Answer:
One of the major component of the atmosphere is water vapour and it plays a very important role in climatic changes and results in precipitation.
![]()
Question 5.
How many types of pollutants are found in the atmosphere?
Answer:
There are mainly two types of pollutants found in the atmosphere
- Gaseous – carbon dioxide and smog
- Solid – dust and bacteria
Question 6.
Which ty pe of pressure are exerted by cold and hot air?
Answer:
The air expands when heated up hence becomes lighter and goes up. Cold air is heavy and dense so it tends to go down and sinks. When hot air goes up and rises, from surrounding areas, cold air rushes to fill the gap.
Question 7.
Explain the temperature in cities are much higher than that of the villages.
Answer:
In the cities, we find many high rise buildings. The fnetals and concretes in these buildings and the asaphalt of roads get heated up during the day and this heat is released in the night.The other important cause is that in the cities the crowded buildings trap the warm air and hence raise the temperature of the cities. Therefore, the temperature in cities are much higher than that of the villages.
Question 8.
Poles are covered with snow always. Why?
Answer:
From the equator towards the poles the amount of insolation decreases. Hence, the temperature decreases in the same manner. This is the reason why poles are covered with snow always..
Question 9.
What do you mean by global warming?
Answer:
Global warming happens when the level of carbon dioxide increases in the atmosphere due to factory smoke or car fumes and the heat retained increases the temperature of the earth.
![]()
Question 10.
Rainfall is important for us when there is excess rain, what happens?
Answer:
For the survival of animals and plants,rainfall is very important. It actually brings fresh water to the surface of the earth. There is water scarcity and drought like situation when there is less rainfall. And, if there is excess rainfall then floods take place which makes the life very difficult to sustain. Many things get damaged such as crops, houses, etc.
Question 11.
In which manner bacteria help plants use nitrogen?
Answer:
For the plant’s survival, nitrogen is very crucial and important. But plants cannot take nitrogen directly from the atmosphere. Hence, bacteria that lives in the soil and roots of some plants take nitrogen from air and changes its form so that the plant can use it.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Discuss the different layers of the atmosphere.
Answer:
The atmosphere has five different layers. They are:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
- Exosphere
- Troposphere:
All the weather characteristics occurs here such as fog, rainfall, hailstorm. This is the thickest and the most important layer of the atmosphere. It has the average height of 13 km. We also find the air which we breathe. - Stratosphere:
It lies just above the troposphere and presents the ideal conditions for flying aeroplanes. Stratosphere extends upto a height of 50 km. It also contains the ozone gas layer which protects us from harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun. - Mesosphere:
It lies above the stratosphere. It extends upto the height of 80 kms. In this layer, meteorites bum up on entering from the space. - Thermosphere:
It lies just above the mesosphere. It extends between 80 400 km. Temperature rises very fast with the increase in height in this layer. In thermosphere, radio waves are transmitted from the earth are reflected back to the earth. - Exosphere:
This is the last and the uppermost layer with very thin air. Light gases such as helium and hydrogen float -into the space from exosphere.
Question 2.
What are the different constituents of air? How they are important to us?
Answer:
The different constituents of air are oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, ozone, helium, argon and hydrogen. Besides these gases, the air also contains some amount of water vapour and dust particles. They are important to us in many ways:
Oxygen:
It is one of the major gas and second most in volume which makes up about 21% of the air. It is also called as life supporting gas. The atmosphere is continuously recharged and restored of oxygen by green plants through the photosynthesis process and thus keeps a healthy and efficient balance of oxygen in the air. Nitrogen: The total volume of nitrogen is about 78% in the air. The major amount of nitrogen is not utilized in our body system when we inhale. But, plants need nitrogen for the well being and survival.
They absorb it through soil and plant roots. Carbon Dioxide: Carbon dioxide is composed of very small percentage around 0.03% of the air. Then also, it is one of the important gas in maintaining the life cycle of plants on the earth. Carbon dioxide absorbs heat of the sun and warms up the lower atmosphere of the surface of the earth. It is taken by the green plants when human beings and animals release it.