Students should go through these JAC Class 9 Maths Notes Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes will seemingly help to get a clear insight into all the important concepts.
JAC Board Class 9 Maths Notes Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes
Solid Figures:
If any figure such as cuboids, has three dimensions length, width and height then it is known as three dimensional figures. Rectangle has only two dimensions i.e. length and width. Three dimensional figures have volume in addition to areas of surface from which these solid figures are formed.
→ Cuboid:
There are six faces (rectangular), eight vertices and twelve edges in a cuboid.
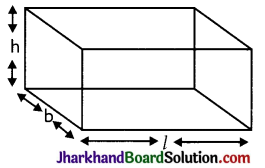
Total Surface Area (T.S.A.): The area of surface from which cuboid is formed. If l, b, h be length, breadth and height of a cuboid respectively then
(i) Total Surface Area (T.S.A.) = 2 [l × b + b × h + h × l]
(ii) Lateral Surface Area (L.S.A.) = 2h (b + l)
(or Area of 4 walls) = 2h(l + b)
(iii) Volume of Cuboid = (Area of base) × height = (l × b) × h
(iv) Length of diagonal = \(\sqrt{l^2+b^2+h^2}\)
→ Cube:
Cube has six faces. Each face is a square.
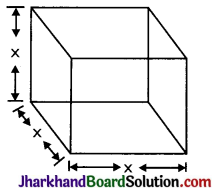
If x is a side of cube, then
(i) T.S.A. = 2[x·x + x·x + x·x]
= 2[x2 + x2 + x2] = 2(3x2) = 6x2
(ii) L.S.A. = 2[x2 + x2] = 4x2
(iii) Length of diagonal = x\(\sqrt{3}\)
(iv) Volume = (Area of base) × Height
= (x2) × x = x3
→ Cylinder:
Curved surface area of cylinder (C.S.A.): It is the area of surface from which the cylinder is formed. When we cut this cylinder, we will find a rectangle with length 2πr and height h units.
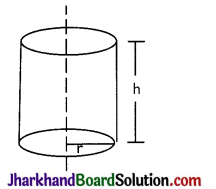
If r be the radius and h be height of a cylinder, then
(i) C.S.A. of cylinder = (2πr) × h
= 2πrh.
(ii) T.S.A.C.S.A. + area of circular top and bottom
= 2πrh+ (πr2) + (πr2)
= 2πrh + 2πr2 = 2πr(h + r) sq.units
(iii) Volume of cylinder
= Area of base × height
= (πr2) × h = πr2h cubic units
→ Hollow cylinder:
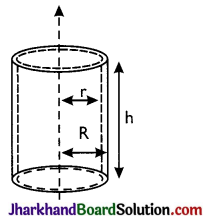
(i) C.S.A. of hollow cylinder
= 2π(R + r)h sq. units
(ii) T.S.A. of hollow cylinder
= 2π(R + r)h + 2π(R2 – r2)
= 2π(R + r) [h + R – r] sq. units
(iii) Volume of hollow cylinder
= π(R2 – r2)h cubic units
Where, r = inner radius of cylinder
R = outer radius of cylinder
h = height of the cylinder
→ Cone:
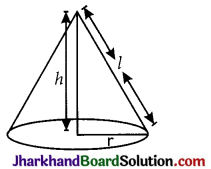
(i) C.S.A. of cone = πrl
(ii) T.S.A.of cone = C.S.A. + Base area
πrl + πr2 = πr(l + r)
(ii) Volume of cone = \(\frac{1}{3}\)πr2h
Where, h = height of cone
r = radius of base of cone
l = slant height of cone
→ Sphere:
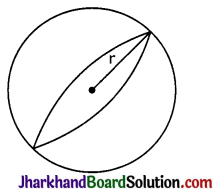
(i) T.S.A. of sphere = 4πr2
(ii) Volume of sphere = \(\frac{4}{3}\)πr3
Where r be the radius of the sphere.
→ Hemisphere:
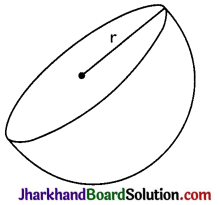
(i) C.S.A. = 2πr2
(ii) T.S.A. = C.S.A. + base area
= 2πr2 + πr2 = 3πr2
(iii) Volume = \(\frac{2}{3}\)πr3
Where r is the radius of Hemisphere
→ Hollow Hemisphere:
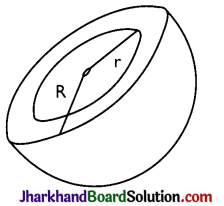
(i) C.S.A. = 2π(R2 + r2)
(ii) T.S.A. = 2π(R2 + r2) + π(R2 – r2)
(iii) Volume = \(\frac{2}{3}\)π(R3 – r3)