JAC Board Class 8th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 5 Industries
JAC Class 8th Geography IndustriesIn Text Questions and Answers
Page 48
Question 1.
Trace the journey of your shirt from a cotton field to your wardrobe.
Answer:
Cotton yam that is used in making cotton garments have to go through a long journey from fields to our wardrobes. The first step is naturally growing cotton in the fields which takes a long time and lot of efforts. Cotton is found in small bud like structures. During harvesting season, farmers pluck out cotton buds and separate raw cotton. The raw cotton is then spinned on a hand loom or power loom. After spinning, cotton yam is weaved to make finished cotton cloth. This cloth is used by tailors to make different garments and sold to retailers. We buy garments from retailers and that is how it reaches us.
Page 49
Question 2.
Give some examples of agro-based industries.
Answer:
Some agro-based industries are tea industry, sugar industry, textile industry, food processing industries.
Page 50
Question 3.
Find out the inputs, outputs and processes involved in the manufacture of a leather shoe.
Answer:
The inputs, outputs and processes involved in the manufacture of a leather shoe:
Input:
Raw material, labour, land cost, transportation cost, infrastmcture.
Output:
Leather shoes
Processes:
Activities to convert hide into leather, washing, cleaning, cutting into different design, sewing, polishing, packing, then out for sale in market.
Page 55
Question 4:
With the help of an atlas identify some iron and steel industries in India and mark their location on an outline map of India.
Answer:
Students need to do it on their own.
Page 58
Question 5.
Collect different types of pieces of cloth from a tailor’s shop and classify them under cotton, silk, synthetic and woolen. Find out the raw materials used in their manufacturing.
Answer:
Students need to do it on their own. Raw material cotton crop silkworm yam wool
Page 58
Question 6.
On an outline map of the world mark the places which provide raw material to cotton textile industry of Osaka.
Answer:
Students need to do it on their own.
JAC Class 8th Geography Industries Textbook Questions and Answers
Answer The Following Questions.
Question 1.
(i) What is meant by the term ‘industry’?
Answer:
The term ‘Industry’ deals with the economic activity that is concerned with production of goods, extraction of minerals or the provision of services.
(ii) Which are the main factors which influence the location of an industry?
Answer:
The main factors which influence the location of an industry are land, labour, water, power, availability of raw materials, transport and market.
(iii) Which industry is often referred to as the backbone of modern industry and why?
Answer:
Iron and steel industry is often referred to as the backbone of modem industry because most of the things are either made of iron or steel or whose products are used as raw materials for other industries.
(iv) Why cotton textile industry rapidly expanded in Mumbai?
Answer:
Cotton textile industry rapidly expanded in Mumbai because of many favourable conditions such as it has warm and moist climate, facility of port for importing machineries, availability of raw materials and skilled labour easily.
Tick the correct answer.
Question 2.
(i) Fort Gloster is located in
(a) West Bengal
(b) California
(c) Gujarat
Answer:
(a) West Bengal
(ii) Which one of the following is a natural fibre?
(a) nylon
(b) jute
(c) acryclic
Answer:
(b) jute
Distinguish between the followings.
Question 3.
(i) Agro-based and mineral based industry
Answer:
| Agro-based industry | Mineral based industry |
| Plants and animal based products are used as raw materials. | Mineral ores are used as raw materials. |
| It provides employment mostly in rural areas. | It provides employment in both mral and urban areas. |
| Examples: jute industry, cotton industry, diary products, etc. | Examples: iron and steel industry, etc. |
(ii) Public sector and joint sector industry
Answer:
| Public sector industry | Joint sector industry |
| These industries are owned and run by the government. | These industries are owned and operated by the state as well as individuals. |
| Examples: Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd., BHEL, Steel Authority of India Ltd., etc. | Examples: Maruti Udyog, etc. |
| These are managed by the workforce appointed by the government. | These are managed by government as well as private employees. |
Question 4.
Give two examples of the following in the space provided:
(i) Raw Materials: ………..and……….
Answer:
plants, ores.
(ii) End products:………. and………..
Answer:
Motorbikes, shoes
(iii) Tertiary Activities:……… and ………
Answer:
Banking, transport
(iv) Agro-based Industries:………… and ……
Answer:
Jute, sugar industry
(v) Cottage Industries: …… and ……
Answer:
Pottery, mats
Answer:
(vi) Co-operatives: and
Answer:
Sudha dairy, Khadi industry
Question 5.
Activity
How to identify a location for establishing an industry :
Divide your class into groups. Each group is a Board of Directors faced with the problem of choosing a suitable site for an iron and steel plant of Developed Dweep. A team of technical experts has submitted a report with notes and a map. The team considered access to iron ore, coal, water and limestone, as well as the main market, sources of labour and port facilities. The team has suggested two sites, X and Y. The Board of Directors has to take the final decision about where to locate the steel plant.
- Read the report submitted by the team.
- Study the map to find out the distances of the resources from each site.
- Give each resource a ‘weight’ from 1 to 10, according to its importance. The greater the ‘pull’ of the factor on the industry the higher the weight from 1 to 10.
- Complete the table on the next page.
- The site with the lowest total should be the most satisfactory site.
- Remember each group of directors can decide differently.
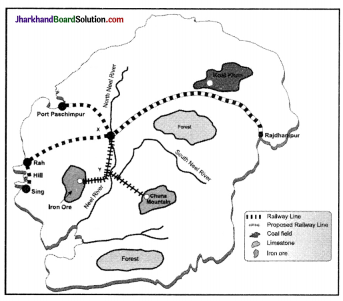
Report Factors/Resources affecting the location of a proposed Iron and Steel Plant on Developed Dweep.
- Iron ore:
This is a very large deposit of low grade iron ore. Long distance transportation of the ore would be uneconomic. - Coal:
The only coalfield contains rich deposits of high grade coal. Transportation of the coal is by railway, which is relatively cheap. - Limestone:
This is widely available over the island, but the purest deposits are in the Chuna Mountains. - Water:
Both the tributaries of River Neel carry sufficient water to supply a large iron and steel plant in all seasons. The sea water because of its high salt content is unsuitable. - Market:
It is expected that the chief market for the Plant’s products will be the engineering works of Rajdhanipur. Transport costs for the products-mainly small steel bars and light steel plates would be relatively low. - Labour supply:
This will have to be recruited mainly from the unskilled workers in the 3 fishing villages of Hill, Rah and
Sing. It is expected that most workers will commute daily from their present homes. - Port facilities:
These are at present minimal. There is a good, deep natural harbour at port Paschimpur developed to import metal alloys.
| Resource | Distance from X | Distance from X | Weighting 1-10 | Distance X weight for site X | Distant X weight for site Y |
| Iron ore | |||||
| Coal | |||||
| Limestone | |||||
| Water | |||||
| Chief market | |||||
| Labour supply | |||||
| Total = | |||||
Students need to do it on their own
JAC Class 8th Geography Industries Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1:
The countries where the textile industries concentrated are…….. .
(a) Japan
(b) India
(c) Taiwan
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 2.
Steel is widely used for industrial purposes because
(a) of ability to resist rusting.
(b) of being tough.
(c) both a and b
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) both a and b
Question 3.
The is a mineral based industry.
(a) coffee
(b) petrochemical
(c) sugar
(d) cotton
Answer:
(b) petrochemical
Question 4.
Public sector plants market their steel through:
(a) SAIL
(b) Tata Steel
(c) TISCO
(d) HAL
Answer:
(a) SAIL
Question 5.
In India, has emerged as the ‘electronic city’.
(a) Bengaluru
(b) Mumbai
(d) Pune
Answer:
(a) Bengaluru
Question 6.
The first cement plant was setup in….. .
(a) Kolkata
(b) Chennai
(d) Delhi
Answer:
(b) Chennai
Question 7.
Silica is used as raw material in industries.
(a) steel
(b) aluminum
(c) cement
(d) none of these
A(c) cement
Question 8.
The largest producer and consumer of steel in the world is/ are
(a) India
(b) China
(c) USA
(d) both b and c
Answer:
(b) China
Question 9.
The challenge that Jute industry facein India is/are:
(a) competition from synthetic substitution.
(b) poor market price.
(c) low productivity of labour.
(d) high cost.
Answer:
(a) competition from synthetic substitution.
Question 10.
Industrial accidents usually happen due to
(a) technical failure.
(b) negligence.
(c) irresponsible handling of materials.
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which industry uses Bauxite as raw material?
Answer:
The industry which uses Bauxite as raw material is Aluminum industry.
Question 2.
Which place/city is known as the ‘Manchester of India’?
Answer:
Ahmadabad is known as the ‘Manchester of India’.
Question 3.
Where was the first textile mill in India established?
Answer:
The first textile mill in the country was established at Fort Gloster near Kolkata.
Question 4.
What are the major hubs of Information Technology industry in the world.
Answer:
The major hubs of Information Technology industry are the Silicon Valley of Central California and the Bangalore region of India.
Question 5.
In which countries iron and steel industries in the world are located?
Answer:
The countries in which iron and steel industry is located are Germany, USA, China, Japan and Russia.
Question 6.
What is the link between the mines and the industry in Pittsburgh?
Answer:
The link between mines and the industry in Pittsburgh is one of the world’s best routes for shipping ore cheaply – the famous Great Lakes waterway.
Question 7.
From where does the iron ore come to Pittsburgh?
Answer:
The iron ore come to Pittsburgh from the iron mines at Minnesota, about 1500 km from Pittsburgh.
Question 8.
What do you mean by sunrise industries? Give examples.
Answer:
Emerging industries are also known as ‘Sunrise Industries’. These industries include Information Technology, Wellness, Hospitality and Knowledge.
Question 9:
Where do we find the major industrial regions of the world?
Answer:
Major industrial regions of the world are eastern North America, western and central Europe, eastern Europe and eastern Asia.
Question 10.
In which year, the industrial disaster occurred in Bhopal?
Answer:
On 3rd December 1983, the industrial disaster occurred in Bhopal.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which industries have replaced the cotton textile industry of Osaka?
Answer:
The cotton textile industry of Osaka has been replaced by other industries, such as iron and steel, machinery, ship building, automobiles, electrical equipment and cement.
Question 2.
What does industrial system composed of?
Answer:
Industrial system composed of the following things:
- input
- processes
- output.
Question 3.
What do you mean by marine based industries?
Answer:
The products from sea and oceans are used as raw materials in marine based industries. Some examples of this industries are manufacturing fish oil, processing sea food.
Question 4.
List the important industrial regions of India.
Answer:
Industrial regions of India are:
- Gurgaon-Delhi-Meerut region
- Mumbai-Pune region
- Ahmedabad-Baroda region
- Chhota Nagpur region
- Bengaluru-Tamil Nadu region
- Vishakhapatnam-Guntur region
Question 5.
Why several textile mills close down in Ahmedabad in recent years?
Answer:
Several textile mills have closed down in Ahmedabad in recent years because of the emergence of new textile centres in the country as well as non-upgradation of machines and technology in the mills of Ahmedabad.
Question 6.
What products do industrial plants in Jamshedpur produce?
Answer:
In Jamshedpur, several other industrial plants were set up after TISCO. They produce chemicals, locomotive parts, agricultural equipment, machinery, tinplate, cable and wire.
Question 7.
Why did the cotton textile industry in India could not compete with the industries in the west initially?
Answer:
The production of handwoven cotton textile was expensive and time consuming. Hence, traditional cotton textile industry could not face the competition from the new textile mills of the West, which produced cheap and good quality fabrics.
Question 8.
List the similar points between information technology industry in Bangalore and California.
Answer:
Similar points between information technology industry in Bangalore and California are:
- Presence of high quality educational institutions and advanced scientific and technological centres.
- Availability of skilled work force.
- Good access to markets.
- Pleasant climate with an attractive and a clean environment.
- Well developed and well connected.
Question 9.
What do you mean by small scale industry?
Answer:
Small scale industries run on small capital and technology that produce large volumes of products such as silk weaving and food processing industries.
Question 10.
What do you mean by secondary activities?
Answer:
In secondary activities or manufacturing, raw materials are changed into products of more value to people. Such as, pulp changes into paper and paper into notebook. These steps represent the different level of manufacturing processes.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
On the basis of ownership, industries can be classified into how many parts? Explain.
Answer:
On the basis of ownership, industries can be classified into 4 sectors. They are private sector, state owned or public sector, joint sector and cooperative sector.Private sector industries are owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals. Examples are Reliance Industries, Adani Groups, Birla Groups, etc The public sector industries are owned and operated by the government.
Examples are Hindustan Aeronautics Limited, Steel Authority of India Limited, BHEL, etc Joint sector industries are owned and operated by the state and individuals or a group of individuals. An example of joint sector industry is Maruti Udyog Limite(d) Co-operative sector industries are owned and operated by the producers orsuppliers of raw materials, workers or both. Example of co-operative venture are Anand Milk Union Limited and Sudha Dairy.
Question 2.
On the basis of raw materials, industries can be classified Explain.
Answer:
On the basis of raw materials, industries can be classified into the following industries: agro-based, mineral based, marine based and forest based Agro-based industries use plant and animal based products as their raw materials. Examples of agro-based industries are food processing, vegetable oil, cotton textile, dairy products and leather industries. Mineral based industries are primary industries that use mineral ores as their raw materials. The products of these industries feed other industries.
Example Iron made from iron ore is the product of mineral based industry and this is used as raw material for the manufacture of a number of other products, such as heavy machinery, building materials and railway coaches. Marine based industries use products from the sea and oceans as raw materials. Some examples are industries processing sea food or manufacturing fish oil. Forest based industries utilise forest produce as raw materials. The industries associated with forests are pulp and paper, pharmaceuticals, furniture and buildings.