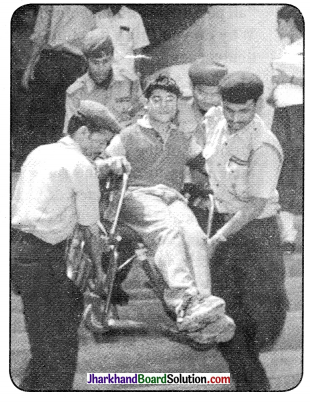
JAC Board Class 7th Social Science Solutions Civics Chapter 2 Role of the Government in Health
JAC Class 7th CivicsRole of the Government in Health InText Questions and Answers
Page 19
Question 1.
Would you associate all or some of these pictures with ‘health’ ? In what ways? Discuss in groups.
Answer:
Students need to do it by themselves.
![]()
Question 2.
Pick two situations from the collage that are not related to illness and write two sentences on how they are related to health.
Students need to do it by themselves.
Question 3.
Can you provide a title to these columns?
Answer:
The titles can be:
- Advancement in Health Care
- Health situation in India
Question 4.
In India, it is often said that we are unable to provide health services for all because the government does not have enough money and facilities. After reading the above left hand column, do you think this is true? Discuss.
Answer:
No, it is not true because after reading the left hand side column, we came to know the following things:
- Healthcare have grown significantly over the years.
- India has the largest number of medical colleges in the world.
- India is among the largest numbers of doctors.
- India is the fourth largest producers of the medicines in the world.
- India gets large number of medical tourists for many countries.
Page 21
Question 5.
Read the story given refer NCERT page-21. Then imagine that you are a Judge in the court. What would you say to Hakim Sheik?
Answer:
Being a Judge, I would try to give a fair judgment. He would be granted his due compensation and the doctors and the hospitals who denied to admit him and do the treatment would be given punishments.
Page 21
The story of Hakim Seikh Hakim Seikh was a member of the Paschim Banga Khet Mazdoor Samity (PBKMS), an organisation of agricultural labourers in West Bengal. One evening in 1992, he accidentally fell off a running train and suffered head injuries. He was in a very serious condition and needed immediate treatment. He was taken to a government hospital in Kolkata but they refused to admit him because they did not have a spare bed.Another hospital did not have the facility or the specialised doctors necessary for his treatment. I
n this way he spent 14 hours in a critical state and was taken to eight different government hospitals, but none of them admitted him. Finally, he was admitted in a private hospital, where he received treatment. He spent a lot of money oy his treatment.Angry and upset over the indifferent attitude of all the hospitals that refused to admit him, Hakim Seikh and PBKMS filed a case in the court.
![]()
Question 6.
Read the story given above. Then imagine that you are a Judge in the court. What would you say to Hakim Seikh?
Answer:
I would pronounce the judgement with due compensation to Hakim Seikh. I would also heavily fine the delinquent hospitals as deterrent punishment for dereliction of duty.
Page 24
Question 7.
Where do you go when you are ill? Are there any problems that you face? Write a paragraph based on your experience.
Ans:
I go to a private hospital or clinic. I prefer it because there is no rush. Doctors give attention to the patients immediately. We get all the services in one place only. Apart from this, the private clinics are neat and clean also. Problems to be face:
- Non-availability of expert doctors on the spot-.
- High cost of treatment.
- No proper guidance and information.
Question 8.
Why did Ranjan have to spend so much money? Give reasons.
Answer:
Ranjan have to spend, so much money because his father took him to a private hospital and got a quick treatment as they are from a well to do family.
Question 9.
What problems did Aman face in the Government hospital? How do you think the hospital can work in a better manner? Discuss.
Answer:
In the public hospital, people always get long queues to wait for their turn. Hence, Aman also had to wait for his turn at the OPD section. He leaned on his father as he was feeling very sick. There turn came after a long wait and the doctor asked to do some blood tests. For blood tests also there was a long queue. They got the test results after three days.Again they visited the doctor but another doctor was on duty on that day and he prescribed the medicines.
In order to avoid these type of situations, there should be more qualified and experienced doctors and medically trained person. Facilities should be improved so that the people get the results little early. More branches of healthcare services should be provided. More mobile clinic should also be opened.
Question 10
What problems do we face in private hospitals? Discuss.
Answer:
In private hospitals we have to spend much more than the public hospitals. We have to buy the medicines from outside which the doctor will prescribe. Most of the time its mandatory to avail the facilities provided by hospital which is costlier then the outside market. Sometimes, some unnecessary tests and medicines are also given for their own profit which is not necessary for the patient.
Page 25
Question 11.
In what ways is the public health system meant for everyone?
Answer:
Public hospitals and health centres have been established by the government to provide healthcare to all citizens. The taxes we pay to the government are used to run these services. Hence, such facilities are meant for every citizen.
![]()
Question 12.
List some Public Health Centres (PHCs) or hospitals near your place. From your experience (or by visiting any one of them), find out the facilities provided and people who run the centre.
Answer:
Students need to do it on their own.
Page 26
Question 13.
How can health care be made more affordable? Discuss.
Answer:
The different ways through which we can make healthcare affordable for all are:
- Opening more numbers of hospitals, healthcare centres, dispensaries and family welfare centres.
- Organizing more camps for the prevention of spreading of diseases such as pulse polio.
- To provide cheaper health services and little early to the poor people.
- Free camps for check up of general public should be increased.
- Among common people, spreading
- health awareness through different means.
- Provisions should be made to deal with unwanted situations like emergency, epidemics and pandemics.
Question 14.
Private health facilities can mean many things. Explain with the help of some examples from your area.
Answer:
Private health facilities can mean many things’. Now a days these hospitals are run by big companies. Such companies
run several businesses associated with these centres such as the facilities of pathology, laboratory, medicines, etc.
JAC Class 7th Civics Role of the Government in Health Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In this chapter you have read that health is a wider concept than illness. Look at this quote from the Constitution and explain the terms ‘living standard’ and ‘public health’ in your own words.
Answer:
Living standard :
it means the standard of living of people at which they live provided by the family or government. It also refers to the status earned by the people. It means that if they are having all comforts of life and live in a hygienic conditions then there standard of living is quite good. Whereas, if the person is not having all the necessary things for the day to day life, bound to live in a filthy and dirty place, drink polluted water and eat unhygienic foods, it means they have a low standard of living.
Public health:
it refers to the health of the general public of the country. It also refers to the-provision of quality healthcare services by the government either free or at low cost.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the different ways through which the government can take steps to provide healthcare for all? Discuss.
Answer:
The different ways through which the government can take steps to provide healthcare for all are:
- Opening more numbers of hospitals, healthcare centres, dispensaries and family welfare centres.
- Organizing more camps for the prevention of spreading of diseases such as pulse polio.
- To provide cheaper health services and little early to the poor people.
- Free camps for check up of general public should be increased.
- Among common people, spreading health awareness through different means.
- Provisions should be made to deal with unwanted situations like emergency, epidemics and pandemics.
Question 3.
What differences do you find between private and public health services in your area? Use the following table to compare and contrast these.
| Facility | Affordability | Availability | Quality |
| Private | |||
| Public |
Answer:
| Facility | Affordability | Availability | Question uality |
| Private | Expensive, very high | Available | Good quality |
| Public | Either free or at low cost | Services are available but it takes long time. | There is always a rush in these hospitals. |
Question 4.
‘Improvement in water and sanitation can control many diseases.’ Explain with the help of examples.
Answer:
The basic necessities for the maintenance of our health are water and sanitation. Poor quality of water causes many health issues such as dysentery, malaria, cholera, diarrhoea, jaundice. Similarly, poor sanitation causes many epidemics and diseases such as plague, dengue. Hence, improvement in water and sanitation can control many diseases. We can do simple things to achieve this such as keeping the water coolers dry, not to store water in pots, change waters in coolers, etc.
JAC Class 7thCivics Role of the Government in Health Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The expected role of government is
(a) Polluting environment
(b) Having clean and pollution free environment
(c) Allowing people to litter around
(d) Providing filthy drinking waters to the people of the country
Answer:
(b) Having clean and pollution free environment
Question 2.
The water borne disease/s is/are
(a) Hepatitis
(b) Worms
(c) Diarrhoea
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
![]()
Question 3.
India is the ……. largest producer of medicines in the world and also a large exporter of medicines,
(a) First
(b) Second
(c) Third
(d) Fourth
Answer:
(d) Fourth
Question 4.
Our country has the money, knowledge and people with experience but cannot make the necessary healthcare available to all its citizens such a situation is known as
(a) Paradox: Something that is contrary .to what would be expected.
(b) Healthy: Free of illness, injury and mental strain.
(c) Mundane: Boring situation.
(d) Personification: Figure of speech
Answer:
(a) Paradox: Something that is contrary .to what would be expected.
Question 5.
RMPs are
(a) Rural Medicine Property
(b) Registered Medical Property
(c) Registered Medical Practitioners
(d) Rural Multiplex Property
Answer:
(c) Registered Medical Practitioners
Question 6.
Costa Rica became a healthy country by using
(a) The money they save by not having an army but spending it on health services and facilities.
(b) Because they only eat vegetarian food
(c) The money they spend on their animals
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) The money they save by not having an army but spending it on health services and facilities.
Question 7.
The healthiest country/ies in South America is/are
(a) Argentina
(b) Chile
(c) Costa Rica
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Costa Rica
Question 8.
One of the major function of public healthcare system is to prevent the spread of dangerous diseases such as TB, malaria, jaundice, cholera, diarrhoea etc. and it is possible when
Answer:
(a) all work is done by the people of the country
(b) the government and the people . work together to achieve this common goal
(c) everything is done by the private sectors
(d) all the work is done by the government
Answer:
(b) the government and the people . work together to achieve this common goal
![]()
Question 9.
Health concerns of are generally ignored.
(a) Men
(b) Women
(c) Children
(d) both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(b) Women
Question 10.
OPD means
(a) Out Patient Department
(b) Ordinary Public Department
(c) Other Patient Department
(d) Other Public Department
Answer:
(a) Out Patient Department
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which state of India guarantee the Right to Healthat first?
Answer:
Assam is the first state of India to guarantee the Right to Health.
Question 2.
What is the percentage of water borne communicable diseases?
Answer:
The percentage of water borne communicable diseases is 21%.
Question 3.
Name one communicable disease.
Answer:
T.B. or tuberculosis is one of the communicable disease.
Question 4.
Name the organisation which is responsible for healthcare policy making in India.
Answer:
The organisation which is responsible for healthcare policy making in India is The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the full form of UNICEF and WHO.
Answer:
The full form of
UNICEF: UnitedNations International Children’s Emergency Fund.
WHO: World Health Organisation
Question 6.
Who runs public healthcare system?
Answer:
Government runs public healthcare system.
Question 7.
In what kind of hospitals patients see long standing queues?
Answer:
Patients and p’eople generally see long standing queues in public and government hospitals.
Question 8.
What do you mean by communicable diseases?
Answer:
Communicable diseases are diseases that are spread from one person to another in several ways such as through water, food, air, etc.
Question 9.
What do you mean by health?
Answer:
Health means leading a good and happy life without mental strain and being active, in positive spirit. Above all, ability to remain free from illness and injuries.
![]()
Question 10.
Where are private health services available?
Answer:
Private health services are available in urban areas.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Who are medical tourists?
Answer:
Medical tourists are the foreigners who come to this country especially for medical treatment at hospitals that offer world-class facilities at a lower cost than what they would have to pay in their own countries.
Question 2.
What is the work of village health workers?
Answer:
There are health centres in the villages where there is usually a nurse and a village health worker. They are trained in dealing with common illnesses and work under the supervision and observation of doctors at the Primary Health Centre (PHC).
Question 3.
What measures can we take to prevent and treat illnesses?
Answer:
The measures we can take to prevent and treat illnesses is that we need appropriate healthcare facilities such as health centres, hospitals, laboratories for testing, ambulance services, blood banks, etc., that can provide the required care and services that patients need in time of emergency.
Question 4.
Government hospitals are less costly and expensive than the private hospitals. Why?
Answer:
Government hospitals are less costly and expensive than the private hospitals because government uses the money which we pay as tax for providing many public health services for the benefit of all citizens. Whereas, the private health services are run for their own profit and the cost of these services are very high.
Question 5.
Do you think poor people fall ill more? If so, why?
Answer:
The poor people are undernourished. These families do not get enough food to eat. They are not provided with the basic necessities such as drinking water, proper housing, neat and clean surroundings, etc. and hence are more likely to fall ill. The expenses on illness make their situation even worse.
![]()
Question 6.
What is medical ethics?
Answer:
Medical ethics means the value that guide and steer medical professionals. These values refers to the justice, honesty, dignity of work practised by the medical professionals.
Question 7.
What do you mean by health insurance?
Answer:
A policy taken by a person in which the insurance company agrees to pay a fixed and specified amount for medical expenses in case of illness or injury in lieu of a regular premium to the insurance company is known as health insurance.
Question 8.
Do you think sufficient and adequate healthcare available to all? Justify.
Answer:
No, sufficient and adequate healthcare is not available- to all. In India, we are facing a situation where private services are rising and increasing but public services are not. Majorly private services are available and that too are concentrated in urban areas. As these services are expensive, many people cannot afford them or have to borrow money when there is an illness in the family.
Women are not taken to a doctor until and unless the matter triggers as women’s health concerns are considered to be less important and valuable than the health of men in the family. Many tribal areas have few health centres and they do not run properly. Even private health services are not available there.
Question 9.
Discuss the positive features of healthcare in India.
Answer:
Positive features of healthcare in India are:
- India has the largest number of medical colleges in the world and is among the largest producers of doctors.
- Healthcare facilities have grown substantially and significantly over the years. In 1991, there were 11,174 hospitals but in 2000, the number grew to 18,218.
- India is the fourth largest producer of medicines in the world and is also a large exporter of medicines.
- India gets a large number of medical tourists from many countries. In
- India, they come for treatment in some of the hospitals which compare with the best in the world.
Question 10.
What is the work or functions of Medical Council of India?
Answer:
The work or functions of Medical Council of India are as follows:
- Registering the medical professionals or practitioners.
- Granting acknowledgement and recognition of medical qualification.
- Monitoring the medical practice in the country.
- Maintaining uniform and good standards of medical education in India.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
We should pay taxes to the government. Why?
Answer:
We should pay taxes to the government because:
- Government uses the tax money for providing many public services such as for healthcare, defence, police, judicial system, highways, etc. for i
the benefit of all citizens. - Taxes fund developmental programmes and services such as education, health care, employment, social welfare, vocational training, etc. required for needy and the disadvantaged citizens.
- Tax money is utilised for relief and rehabilitation in case of natural disasters such as flood, epidemic, drought.
- Space, nuclear and missile programmes are also funded from the revenues collected as the taxes from the citizens.
- Government provides some services especially for the poor who cannot afford to purchase them from the market.
- In healthcare system as well medicines and other facilities are in the government hospitals. This is done by the revenues which are collected from tax.
Question 2.
Distinguish between public health services and private health services.
Answer:
The difference between public health services and private health services are:
| Public health services | Private health sen ices |
| The public health . service is a series of health centres and hospitals run by the government. | Private health services are not owned or controlled by the government. It runs privately. |
| It is meant to provide quality healthcare services either free or at a low cost so that even the poor can get proper treatment. | These services are run for profit, the cost of these services is very high and expensive. |
| Public health services are present in rural as well as in urban areas. | Private health services are concentrated mainly in urban areas. |
| Patients usually have to wait in long queues in public hospita | People do not face such problem in private hospitals. |
Question 3.
Discuss the healthcare policy of Kerala government in 1996. Did they succeeded fully?
Answer:
The healthcare policy of Kerala government in 1996 were as follows:
- Forty per cent of the entire state budget was given to panchayats so that they could plan and provide for their requirements.
- Now the villages could make sure proper planning for water, food, women’s development and education.
- This meant that water supply . schemes were checked, the working . of schools and anganwadis were
ensured and specific problems of the village were taken up. - Health centres were also improved. No they didn’t succeeded fully though the situation improved a lot. There were loopholes such as shortage of medicines, hospital beds and less number of doctors and workers.